In-depth Insights: Uncovering User and System Requirements through Modern Discovery Techniques
Welcome back to our exploration of discovery techniques for eliciting user requirements and system requirements! In this continuation, we delve deeper into methodologies and frameworks to understand user needs and preferences, which are essential for successful product development and innovation.
Continuing our research, let's delve into the invaluable method of discovery techniques for eliciting user requirements. Derived from User Experience Design (UXD) and User-Centered Design (UCD), User Journeys offer a profound understanding of user interactions and experiences with a product or service.
Discovery Techniques For Eliciting User Requirements

User Journeys: A Closer Look
User Journeys visually represent the user's interactions and experiences while using a product or service. They aim to capture the user's perspective, emotions, actions, and touch-points across different product interaction stages. By mapping out the user's journey, designers can gain valuable insights into their needs, pain points, and opportunities for improvement. As an integral part of the design thinking process, User Journeys are particularly useful in the "Empathize" and "Define" stages.
Here's how User Journeys fit into the design thinking process:
Empathize Stage
Understanding User Needs In the design thinking process, the first stage is "Empathize," where designers aim to deeply understand the users' needs, emotions, and experiences. User Journeys are instrumental in this stage as they create a detailed visualization of the user's interactions, thoughts, and feelings. By empathizing with users through their journey, designers can gain a deeper understanding of their pain points, challenges, and opportunities for improvement.
User Journeys allow designers to step into the user's shoes and experience the product or service from their perspective. This empathetic approach helps uncover insights that may not be apparent through other methods. By identifying the user's emotions, motivations, and goals at each touchpoint, designers can better address their needs and create a more user-centered solution.
Define Stage
Refining the Problem Space After comprehensively understanding the user's journey, designers move on to the "Define" stage. This stage involves refining the problem space and defining the problems that must be addressed. User Journeys contribute to this process by providing valuable insights into key touch points, bottlenecks, and areas of focus.
By analyzing the user journeys, designers can identify pain points and areas where the user experience can be enhanced. This information helps formulate design challenges and define the specific problems that need to be solved. User Journeys act as a guide, ensuring that the design process addresses the user's needs and creates a solution that truly resonates with them.
Kano Analysis
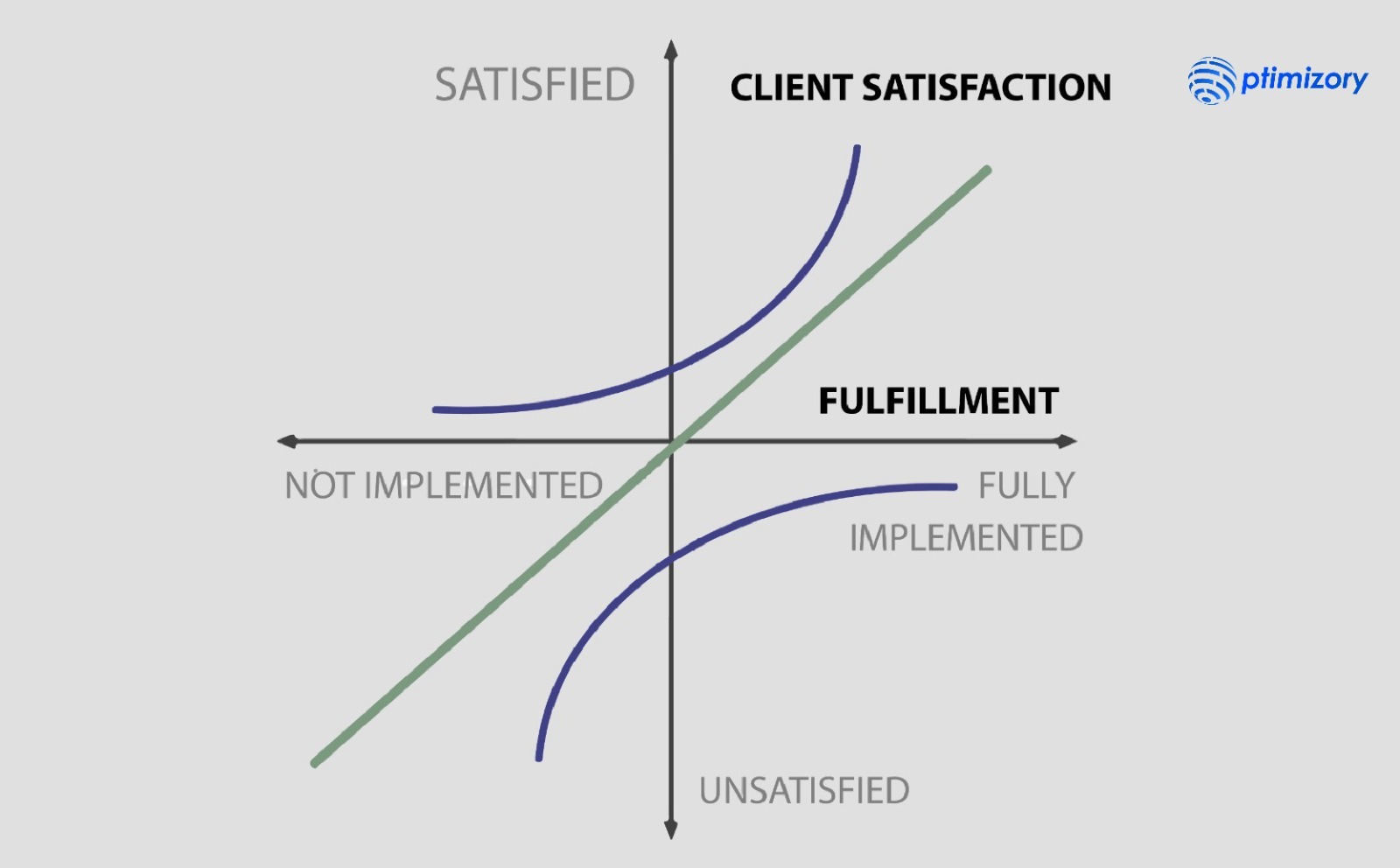
Kano Analysis is a widely used framework in product management and customer satisfaction management. Developed in the 1980s, it remains relevant for understanding customer preferences and prioritizing product features. This analysis categorizes features into five distinct categories, each impacting customer satisfaction.
-
Basic Needs: These are essential features that customers expect to be present in a product or service. Their absence leads to dissatisfaction, but their presence doesn't significantly increase satisfaction. Meeting these basic needs is crucial for avoiding customer dissatisfaction.
-
Performance Needs: Performance needs are features where the relationship between the feature's level and customer satisfaction is linear. In other words, the better the feature, the more satisfied customers are. Improving these features can directly enhance customer satisfaction.
-
Excitement Needs: Excitement needs are unexpected and delightful features that can significantly enhance customer satisfaction when present. However, their absence doesn't lead to dissatisfaction. These features exceed customer expectations and can create a positive emotional response, delighting customers and differentiating the product from competitors.
-
Indifferent Needs: Indifferent needs are features that don't significantly impact customer satisfaction, whether they are present or not. Customers are neither satisfied nor dissatisfied with these features. While they may not be a priority for improvement, they should still be considered in the overall product offering.
-
Reverse Needs: Reverse needs are features that, when present, can lead to customer dissatisfaction. These features may not align with customer expectations or may have negative consequences. Identifying and addressing these features is crucial to avoid customer dissatisfaction.
Using Kano Analysis, businesses can prioritize feature development based on their impact on customer satisfaction. It helps product managers and designers decide which features to focus on and how to allocate resources effectively. Additionally, Kano Analysis recognizes that customer preferences are dynamic, and what may be an exciting need today could become a basic need as customer expectations evolve.
Continuous Interviews
Continuous interviews play a vital role in eliciting the requirements of a product or service. Teresa Torres has introduced the concept of "continuous discovery habits," emphasizing the importance of interviewing and engaging with customers throughout the product development process, not just in the early stages. This approach suggests conducting interviews regularly, ideally weekly, to uncover and understand the actual needs of customers continuously.
Figure below illustrates a sample template that can be used to structure and organize the information obtained from the continuous interviews.

The key shift in conducting continuous interviews is the focus of the questions. Instead of solely asking customers what they want, the emphasis is on exploring their past experiences to identify opportunities for improvement. By delving into their previous interactions and understanding their pain points, businesses can uncover valuable insights that can shape the development of the product or service.
To effectively capture the information gathered during these interviews, it is recommended to use a template for interview notes. This template should align with the desired outputs of the interviews.
The Mom Test
The "Mom Test" by Rob Fitzpatrick challenges the common mistake of focusing interviews on the solution. Instead, it emphasizes asking the right questions to uncover genuine insights. By framing questions around past experiences, interviewers can discover opportunities and understand the true problem. The key is to listen more, empathize, and avoid imposing personal ideas. The goal is to gather valuable feedback and develop solutions that address real customer needs.
Opportunity Solution Trees
Opportunity Solution Trees, a technique introduced by Teresa Torres, complemented customer interviews in identifying potential opportunities for our product. These trees serve as visual representations of solutions to customer problems. The process involves breaking down the problem into smaller opportunities, brainstorming multiple solutions for each opportunity, and evaluating and selecting the most promising solution
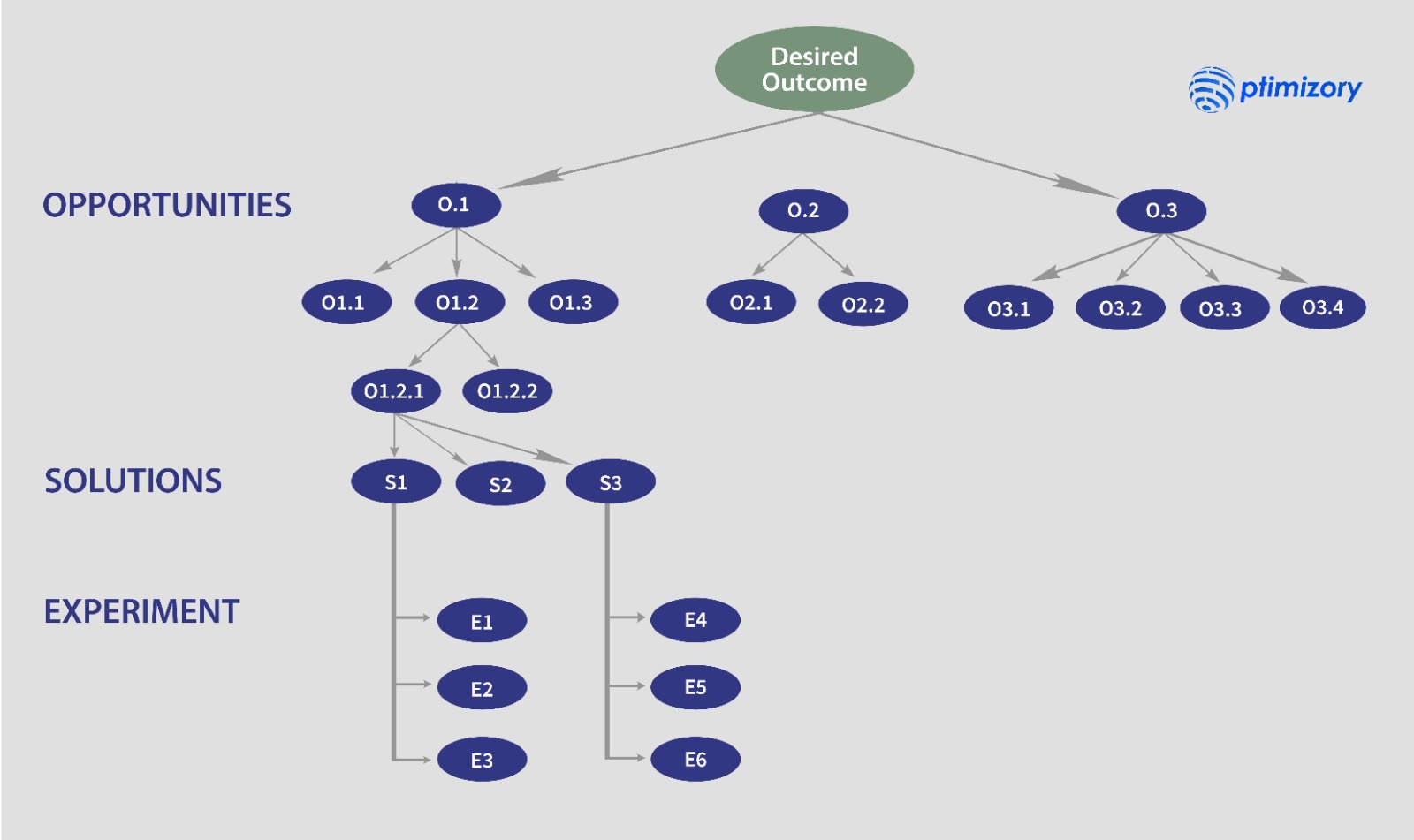
We can systematically explore various avenues to address customer needs by utilizing opportunity solution trees. This approach allows us to generate various potential solutions and evaluate their viability. By selecting the most promising solution, we can focus on developing a product that effectively solves the identified problem.
Discovery Techniques For Elicitation Of System Requirements
Discovery techniques for elicitation of system requirements play a crucial role in understanding and capturing the needs of stakeholders. These techniques help uncover valuable insights that shape the development of practical solutions. Here are a few commonly used techniques:
User story mapping
User story mapping is widely used in requirements engineering, business analysis, product ownership, and product management. It involves collaborative discovery to understand how a set of user stories addresses a customer problem. The process includes sequencing the user's activities and allows for further elicitation to capture detailed stories and tasks (Figure below). This ensures that the solution aligns with the user's presented activities and needs.
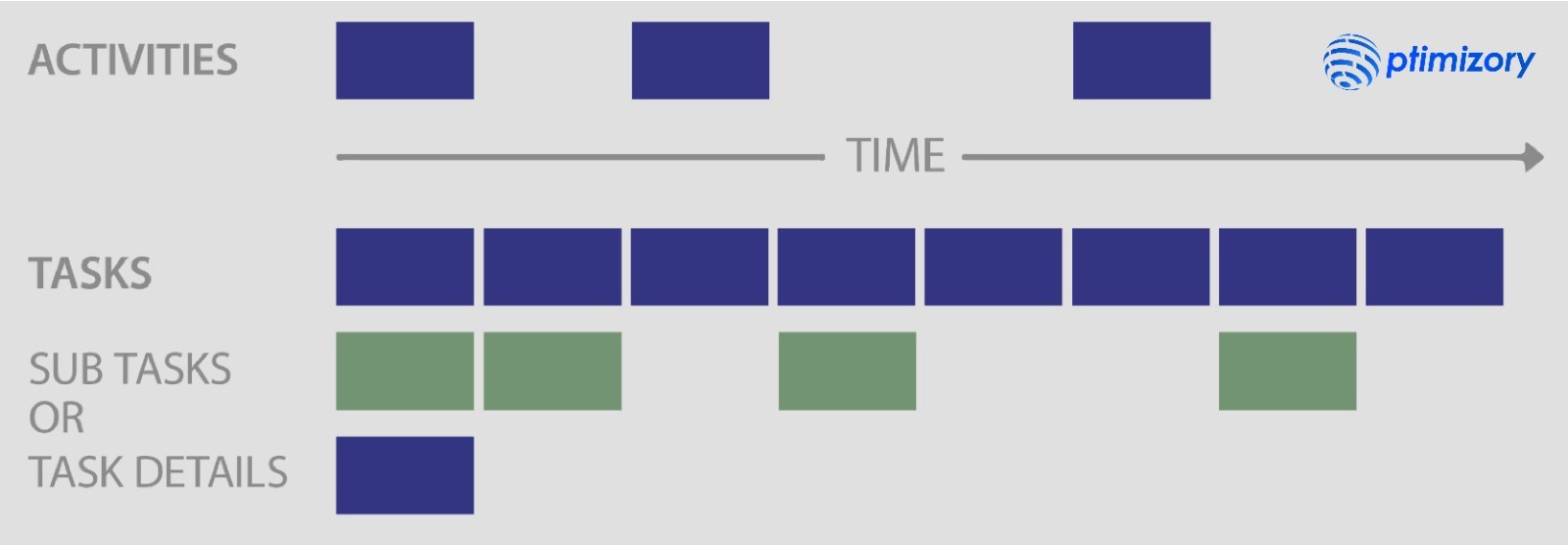
By utilizing user story mapping, teams can comprehensively understand the user's journey and identify the necessary features and functionalities to address their needs. This technique promotes collaboration and helps capture the complete picture of the system requirements, enabling the development of a solution that meets the user's expectations.
Epic Alignment
"Epic alignment," introduced in Nils Janse's book of the same name, presents a valuable approach to establishing a single source of truth for requirements through lightweight documentation centered around epics. This documentation structure progressively adds information about a specific epic throughout the various stages of product development, including Ideation, Discovery, Prioritization, Refinement, Development, and Testing.
The proposed structure of these documents enables a clear understanding of an epic by providing insights into the associated user stories and the necessary implementation details (Figure below). By encompassing information about epics, stories, and details; this approach ensures the inclusion of all three types of requirements: business, user, and system.
Wrapping Up
In conclusion, product discovery is a customer-focused approach that aims to deliver valuable products or services by understanding customer problems, needs, and behaviors. It involves creating a dynamic product backlog based on customer feedback, insights, and experimentation. This shift in requirements elicitation allows for greater flexibility and adaptability to changing customer needs. Techniques such as user story mapping, interviews, workshops, prototyping, and document analysis are used to understand user needs better and create innovative solutions. Organizations can improve customer satisfaction and deliver successful products by embracing product discovery.